Ongoing payroll tasks
In this section we look at the main activities associated with running a payroll, including making submissions to HMRC, paying your employee and paying HMRC.

Content on this page:
Payroll tasks: overview
As an employer, you need to complete certain tasks on an ongoing basis. It may be helpful to think of the tasks that you need to do in a process chart:
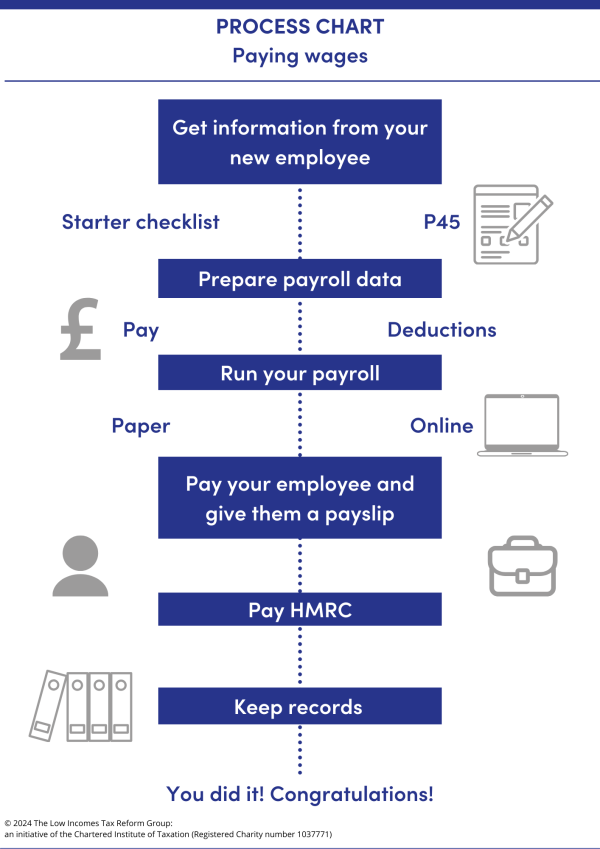
We provide individual pages of guidance looking at some of the main ongoing tasks associated with running a payroll including:
End of tax year tasks
There are also several end-of-year tasks to be aware of. For example, certain forms need to be completed by employers after the end of the tax year. We look at these requirements in more detail in our end of year payroll processes section.
Errors and penalties
For information on penalties under RTI, including for not operating PAYE at all, not doing payroll tasks at the correct time, or not doing them accurately, go to our dealing with PAYE errors page.



