Getting paid
Not sure what your payslip should look like and what information it should contain? We provide you with an example and breakdown of a typical payslip. We also discuss being paid in cash.
Content on this page:
Introduction
It is a legal requirement for your employer to give you, as an employee, a payslip each payday. How often you get a payslip will depend on how often you are paid. It is usually weekly or monthly.
If you are a worker, you also have a legal right to an itemised payslip every pay day. You can read more about what it means to be a ‘worker’ on our page on employment rights. This right exists even if you don’t earn enough money for there to be any deductions made.
The payslip can be a paper form or in electronic form, for example a PDF file.
If your employer does not give you a payslip each payday, you should ask for one. You can bring a claim in the Employment Tribunal if your employer doesn’t provide you with a payslip.
Payslip information
The payslip must show several things, by law. The main ones are:
- your gross wages (the amount before anything is taken off)
- the income tax and NIC deducted under PAYE, any other fixed deductions from gross pay (suitably itemised)
- the number of hours you worked (if your pay varies depending on time worked)
- your net wages (the payment you receive).
It may also show your National Insurance number (NINO), your PAYE code (more on this below), your employer’s PAYE reference, and how you will be paid - for example, in cash, by cheque or directly to your bank. You can find more information from ACAS.
You should check the personal information on your payslip carefully – we discuss this in more detail below under the heading ‘Checking your payslip’.
Understanding your payslip
Note that not all payslips look the same, but they should all contain similar types of information.
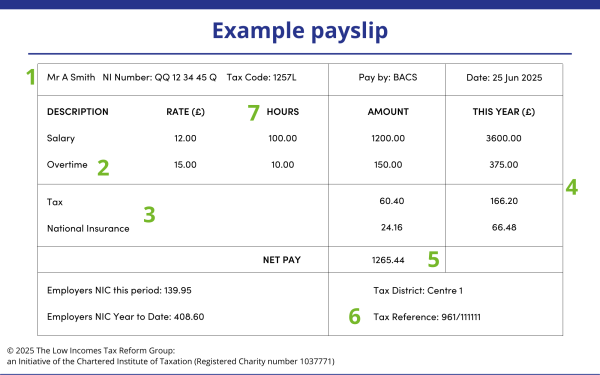
| 1 | Personal information, including name, National Insurance number (NINO) and pay as you earn (PAYE) code |
| 2 | Payments including salary, wages, bonuses, and overtime for the pay period |
| 3 | Deductions including income tax, National Insurance contributions (NIC) and personal pension contributions (if any) for the pay period |
| 4 | Amounts earned and deductions taken off for the tax year to date, including the current pay period. Note that in this example, we have assumed the employee earned different amounts each month, so the year-to-date totals are not simply three times the June amounts. |
| 5 | Net pay for the pay period: this is the payment you should receive. This is your earnings for the pay period less the deductions for the same period |
| 6 | Tax Reference: this is the employer's PAYE reference. Although it is not required by law, it is often included on a payslip. |
| 7 | Hours worked: since April 2019, payslips are required to state number of hours being paid where wages vary according to time worked; either as an aggregate number of hours or as separate figures for different types of work (or rates of pay) |
Sometimes payslips will show the amounts that your employer has paid in employer NIC for your information on your payslip – but it should not be deducted from your pay.
For help with understanding the payslip entries if you work through an umbrella company, see our guidance for umbrella company workers.
Checking your payslip
Here are some questions to ask yourself when looking at your payslip. These will help you check that your payslip is correct.
- Are your name and National Insurance number correct?
- Was the gross pay calculated correctly? You may need to check hours worked and the rate of pay. You should also satisfy yourself that you are being paid at least the appropriate national minimum wage.
- Was the net pay sum actually paid to you? You may need to check your bank statement. If your net pay amount per your payslip and your net pay amount per your bank statement differ, do you understand why? If you don’t understand why, you should seek some advice.
- What tax code is being applied to your earnings? Is it the correct one?
- As said above, although not actually required by law, most employers do include helpful information on payslips like the tax code in operation, and year to date figures, to aid transparency and help you reconcile the figures. If your payslips are not ‘fulsome’ or are hard to follow, then ask yourself why.
You should also carefully check any deductions that have been made. As well as tax and NIC, you may see:
- pension contributions, if you are a member of a workplace scheme, including schemes introduced as a result of auto-enrolment,
- student loan repayments, and
- anything else that you have authorised your employer to deduct (for example costs of disclosure checks, uniforms, or union costs).
If you are concerned that an unauthorised deduction has been made from your wages (an unauthorised deduction can include not receiving any of the pay you were expecting at all), you should look at GOV.UK and ACAS.
Although many payslips are now provided online (more on this below in ‘How to get your payslips’, which means they aren’t as easy to check on a regular basis, it is worth going in and checking them. Although your net pay may look roughly right, employers can make mistakes. These are not always easy to spot from just looking at your net pay amount. Some employers even manipulate people’s pay and taxes to benefit themselves, as we explain here. Checking your payslip will give you a better chance of dealing with any issues or problems before they get out of hand.
Other reasons payslips are important
- You can check you are being paid correctly – you may need to check hours worked and the rate of pay. If you are on the minimum wage and think you have been underpaid, HMRC may ask to see your payslips, so they can investigate your employer.
- You might need them to complete a tax return or to apply for a tax refund – for example, to complete a form P87 to get tax relief on your employment expenses, it is now mandatory to provide your employer PAYE reference number, which can often be found on your payslips.
- Your payslips provide proof of your earnings – which is something that you must have when applying for a mortgage or looking to rent a property. You may also have to show them when applying for a loan or other financial products.
- They might come in useful if you are planning to change jobs – some employers may ask you to provide a few recent payslips as proof of current income when you are negotiating your new salary.
- They are ‘evidence’ if PAYE goes wrong – it is not unusual for the PAYE system to result in you paying the wrong amount of tax. But occasionally you may pay the wrong tax under PAYE because HMRC or your employer have made a mistake. Your payslips may be a key part of the evidence as to what has happened and who, if anyone, is at fault. You may need professional help to sort it out. In almost all instances, the better information an adviser receives (by way of payslips), the quicker and easier they will be able to assist.
- They provide proof of deductions – very occasionally the deductions (including tax and National Insurance) your employer makes from your wages can go missing – either because HMRC ‘lose’ them in their systems (for example they allocate them incorrectly) or because employers fail to pay them over. In these instances, HMRC may well credit you with the relevant amounts but only if you show evidence that the deductions were made. This is particularly important for National Insurance, so that you don’t have gaps in your record. What’s the best form of evidence? You guessed it – payslips!
- They can help you prove your identity – for example if you want to access government online services via the Government Gateway. You can use information from payslips dated within the last 3 months to help prove your identity. If you can’t pass the identity checks then you will not be able to access online services, which could be an inconvenience to you.
- They can prove loss of earnings – if you’re involved in an accident or become ill and seek compensation or to draw down on some kind of protection policy, you may be asked for your payslips as proof of what you will lose in earnings.
How to get your payslips
Your payslip may come in different formats, such as on paper or electronically. Many employers send password-protected payslips by email for security reasons. Some employers place payslips in an online secure storage facility that you can access with personal login details. We know it is easy to forget login details and passwords, but it is important that you can access your payslips. If you leave a job, make sure you download copies of all your electronic payslips before you leave, as you may no longer be able to access them online after you have left.
One complaint we hear a lot is ‘I’ve left my employer and I’ve lost access to all my online payslips’. It is a good idea to try and save copies of your payslips as they are published. However, if you haven’t done this, speak to your ex-employer on this – some systems have admin settings that can be changed to give ex-employee’s certain permissions for a period of time.
If you do not have access to your payslips, provided that your employer submitted the relevant information to HMRC via Real Time Information (RTI), then you may be able to access the details via your personal tax account.
Once you are logged in, you should click on ‘Pay As You Earn (PAYE)’, ‘Check current tax year’, ‘View or update employment details’ and then ‘Check payments received’ under ‘Income received to date’. You should then be able to view year to date figures for taxable income, income tax paid and NIC paid.
If you don’t have it set up on your phone yet, HMRC’s App allows you to check what has been reported in terms of employer payments, tax and NIC in just a few clicks. The App may even be able to display the latest real time payroll information from your employer, before you get your payslip.
Keeping your payslips
Even after you have checked the net amount of pay against your bank statement or pay packet, you should keep your payslips to ensure the totals shown on form P60 at the end of the tax year agree with the sums actually paid.
After that, although there are no hard and fast rules, it’s really in your best interests to keep hold of your payslips – and for as long as possible. Note that people who are required to submit a tax return have a legal obligation to keep them for a certain period.
While employers are obliged by HMRC to keep payroll information (which payslips are part of) for three years from the end of the tax year they relate to, there is no guarantee that your employer will be around to help you with payslip-related requests or will be willing or able to provide you with duplicates.
Being paid in cash
As an employee, you may be paid in cash. However, this does not affect whether you are liable to tax and NIC on your earnings.
You should always receive a payslip each time you are paid, even if you are paid in cash.
Your employer should still take off the right amount of income tax and NIC under PAYE, and hand this over to HMRC before paying you what is left.
Most employers in the UK now pay their employees by bank transfer, although some employers continue to pay in cash.
No payslip
It is possible that an employer may wish to pay their employees in cash so that they can try to avoid their obligations under PAYE (deducting tax, NIC and paying employers’ NIC). They may not pay over any income tax and NIC to HMRC, to save money – this is illegal.
It is important to be aware of the following:
- If your employer fails to meet their obligations under PAYE, HMRC can demand the income tax and NIC from you later in certain circumstances.
- If your employer does not pay over NIC to HMRC for you, you may lose out on state benefits.
It is likely that your employer will not provide you with payslips if they are trying to avoid their obligations under PAYE.
If your employer does not give you a payslip each payday, you should ask for one. You can bring a claim in the Employment Tribunal if your employer doesn’t provide you with a payslip.
Employer acting illegally
If you think your employer is acting illegally you should report them to HMRC. You can find more information on GOV.UK.
Self-employment
If you receive cash payments for work that you carry out as a self-employed person, then the payments are taxable. You must include them when working out your taxable profits for your self-employment and declare them in your annual self assessment tax return.
More information
There is some information on payslips on GOV.UK.
For information on the statements you should get if you work in the Construction Industry Scheme, see our page Construction industry scheme (CIS).



